Goods transport The Netherlands
Goods transport The Netherlands. Goods transport from the Netherlands, to the Netherlands. From the Netherlands we
transport automotive components, but we also provide e.g. the transport of Holland flowers and other goods.
Goods transport from the Netherlands and to the Netherlands. The Netherlands is an open economy with limited state interventions since the 80´s. It is the 16th biggest economy in the world based on the GDP per inhabitant.
The basis of Holland economy is industry, trade and transport. Agriculture also plays a certain role. Dominant sectors in industrial production are processing industry, chemical industry, oil processing and electrotechnical industry.
The financial and trade centre of the Netherlands is Amsterdam. The Amsterdam Stock Exchange (AEX, nowadays a part of Euronext) is one of the oldest stock exchanges in the world. The currency in the Netherlands is Euro. It replaced gulden on 1st January 2002.
The Netherlands does well in trade and transport thanks to its geographical position.
Goods transport The Netherlands
There is the second biggest port in the world in Rotterdam called Europort. It is the biggest port in Europe and it has been the most used port in the world until recently. The port Europort covers the area of 4,000 ha, the whole complex of port buildings and mechanisms approximately 10,000 ha and it is the biggest and the most visited attraction in Rotterdam. Nowadays approximately 40,000 ships sail trough the port, some of them with displacement of 28,000 tons (statistically one ship come throught the entry and exit of the port every 8 minutes). The goods turnover for 1998 was more than 300 millions tons of transloaded load. It is more than in Hamburg, Bremen, London, Marseilles and Bordeaux in total.
Agriculture – fertile soil 27 %, pastures 32 %, forests 9 %
– it forms 4% of GDP
– very intensive, productive and advanced
– cultivation of tomatoes, sugar beet, cereals
– more than 4.5 millions dairy cows are bread on polders
– the 5th place in the butter production in Europe, 4th place in cheese production and 1st place in the production of flower bulbs
– the export of tulips, daffodils, which are grown on polders; high quality salad grown mainly in greenhouses
Industry
– companies with the highest turnover: Shell-oil, Unilever-food and chemistry, Philips-electronics, Akzo-chemistry
– the most important sectors are: engineering – production of electronics, planes and ships, petrochemistry, textile industry and metallurgy – steel production
– minor industry – processing of diamonds – is in Amsterdam
– heavy industry, such as oil refining, steel production, engineering are situated on the coast or close to rivers and channels, mainly in Rotterdam, Ijmunden, Amsterdam, Dordrecht, Arnhen and Nijmengen; the Netherlands was the biggest polluter of the North Sea in the mid-90´s
Goods transport The Netherlands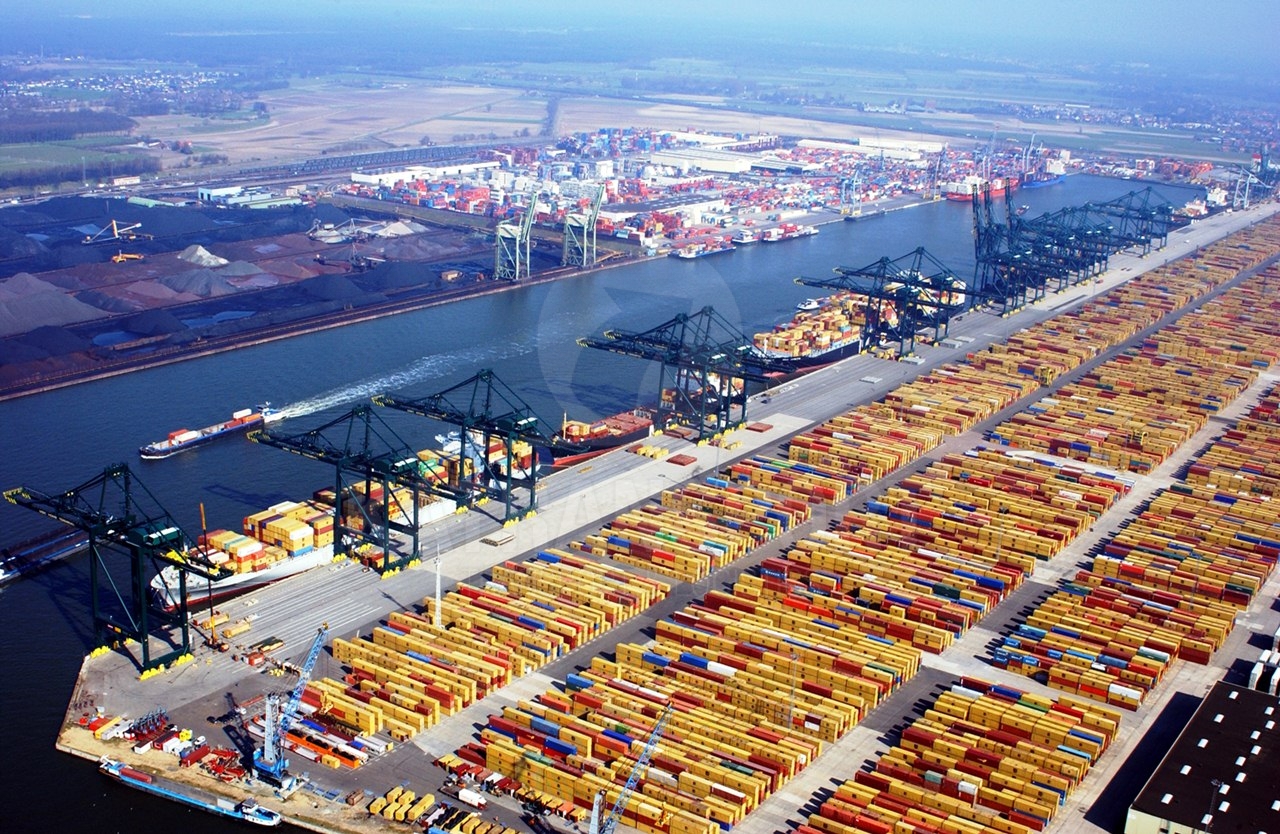
Transport
Roads and motorways: A perfect network of more than 2,000 km of highways (no fees) and approximately 120,000 km of other roads. A green sign E marks an international highway, a red sign A is a national highway and a yellow sign A is the first class road. Speed limit in villages is 50 km/h, on other roads 80 km/h and on highways 120 km/h. Speeding tickets are 40-200 Euro. The main road is signed only exceptionally, so you have to pay attention to small streets on the right, because the right hand rule is applicable. A dense bicycle traffic requires a lot of attention. In case of an accident between a car and a bicycle, a driver is usually guilty. Traffic police is very strict. There are harsh punishments for bad parking. The limit of 0.5 per mil of alcohol in blood is tolerated, but you cannot count on that. There are long traffic jams in rush hours. If a foreigner travels by a rented car, he has to have a notarised permit from the owner of the car in Dutch, German or English.
Rail transport: modern dense network. Nederlandse Spoorwegen has two types of trains: InterCity high-speed trains and local trains. The Netherlands has 2,753 km of railways, 1,987 km of them are electrified
Air transport: small Netherlands has 6 airports with regular transport. Apart from the connections to neighbouring countries, they mainly serve for collection transport to Amsterdam, one of five most important European air hub. The airport is on polders and backfills on the sea, runways and areas are 4 meters below the sea level. The major domestic transport company is royal airline company KLM, the oldest company in the world. It formed the biggest airlines in the world after the fusion with Air France.
Ferry transport: it serves for the transport between islands and the continent. Maritime transport. The Netherlands manages a big part of the maritime transport of Western Europe, 5,052 km of navigable rivers and channels